Managing Muscle Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Muscle pain, often characterized by soreness, stiffness, or aching, is a prevalent health issue that can affect people of all ages and activity levels. While it may seem like a temporary discomfort, persistent muscle pain can significantly impact daily life, reducing mobility, and affecting overall well-being. Understanding the underlying causes, seeking appropriate diagnosis, and implementing effective management strategies are crucial for alleviating muscle pain and promoting optimal recovery.
Common Causes of Muscle Pain
Muscle pain can arise from various factors:
- Overexertion Excessive physical activity or strenuous exercise.
Injuries Strains, sprains, or muscle tears. - Inflammation Conditions like arthritis or tendinitis.
- Neurological Disorders Certain neurological conditions can cause muscle weakness and pain.
- Medical Conditions Underlying health issues, such as thyroid disorders or fibromyalgia.
Symptoms of Muscle Pain
Muscle pain can manifest in different ways:
- Acute Muscle Pain Sudden onset, often associated with injuries.
- Chronic Muscle Pain Persistent pain lasting several weeks or months.
- Localized Pain Pain concentrated in a specific muscle or area.
- Diffuse Pain Widespread muscle pain affecting multiple areas.
- Associated Symptoms Muscle weakness, stiffness, or tenderness.
Diagnosis of Muscle Pain
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment:
- Medical History Detailed information about the onset, duration, and severity of pain.
- Physical Examination Assessing muscle tenderness, strength, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound to rule out underlying conditions.
- Blood Tests Identifying potential inflammatory or metabolic causes.
Treatment for Muscle Pain
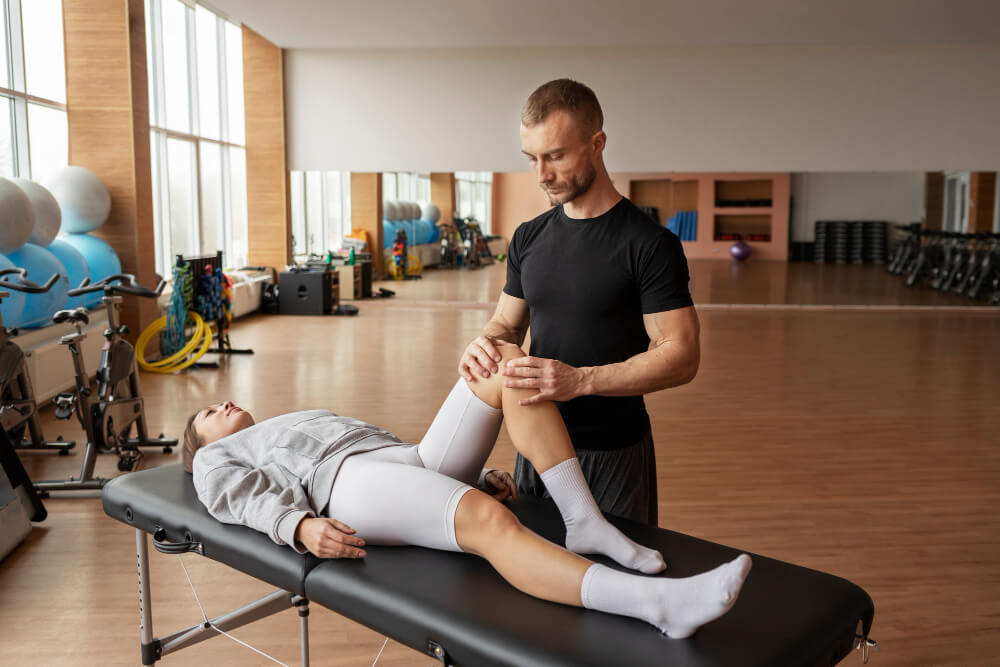

Treatment options for muscle pain vary depending on the underlying cause and severity:
- Rest and Ice Resting the affected muscle and applying ice packs to reduce inflammation.
- Heat Therapy Applying heat to relax muscles and improve blood flow.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Prescription Medications Muscle relaxants or pain relievers for severe pain.
- Physical Therapy Exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Massage Therapy Relieving muscle tension and promoting relaxation.
Preventing Muscle Pain
Adopting preventive measures can help reduce the risk of muscle pain:
- Warm-up and Cool-down Engaging in light exercise before and after physical activity.
- Proper Posture Maintaining good posture to avoid strain on muscles.
- Gradual Exercise Increasing exercise intensity gradually.
- Adequate Hydration Staying hydrated to support muscle function.
- Stretching Regular stretching can improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
By understanding the causes of muscle pain, seeking appropriate treatment, and incorporating preventive measures into daily life, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve overall well-being.