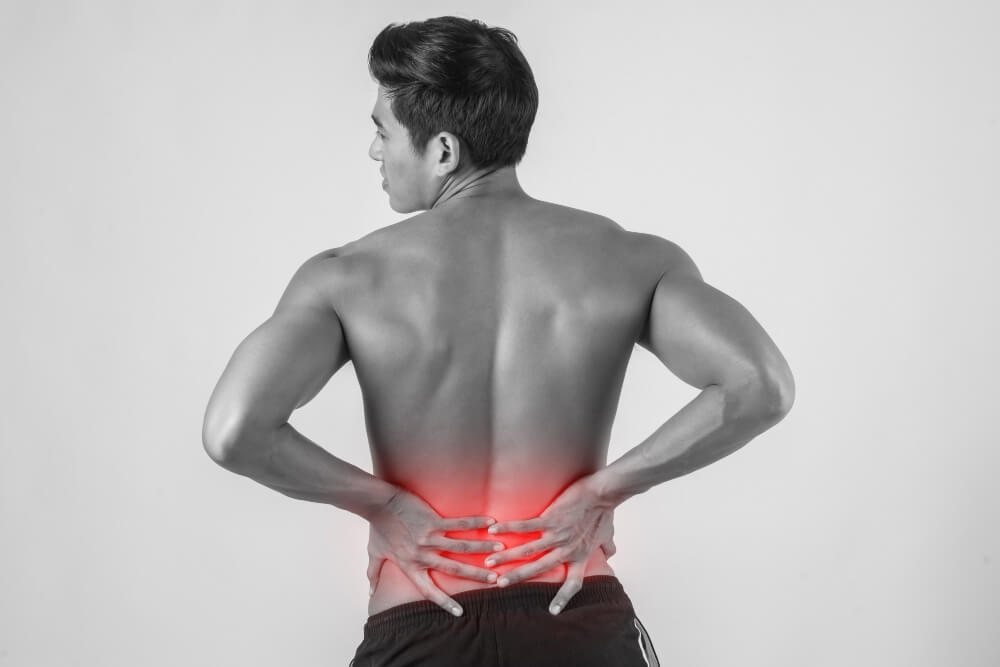
Back Pain and Back Arthritis:
Understanding the Challenge and Finding ReliefBack pain is an excruciatingly common experience, affecting millions worldwide. It can range from a mild, occasional discomfort to a debilitating, chronic condition that significantly impacts daily life. Among the various causes of back pain, arthritis in the back, also called spinal arthritis, stands out as a major contributor. This article delves into understanding back pain, back arthritis, and the diverse treatment options available to manage and improve your well-being.
Understanding Back Pain
Back pain can manifest in various ways, including:
- Aching or dull pain: This is the most common type, often described as a constant ache or tightness in the lower back.
- Sharp or stabbing pain: This type of pain can be sudden and intense, often radiating down the legs (sciatica).
- Burning or stinging pain: This sensation can be localized and uncomfortable, affecting specific areas of the back.
The location of pain also offers clues about its source:
- Lower back pain: This is the most frequent location for back pain and often related to muscle strain, disc problems, or arthritis.
- Upper back pain: This pain can originate from muscle tension, poor posture, or underlying medical conditions.
- Middle back pain: This is less common and may be due to injury, strain, or specific conditions affecting the spine.
Recognizing Back Arthritis
Arthritis refers to a group of conditions characterized by joint inflammation, pain, and stiffness. It can affect any joint in the body, including those in the spine. Different types of arthritis can impact the back, with the two most common being:
- Osteoarthritis: This is the wear-and-tear type of arthritis that develops due to the breakdown of cartilage, the cushioning tissue between spinal bones. It’s more common in older adults but can occur at any age.
- Spondyloarthritis: This encompasses several inflammatory types of arthritis, including ankylosing spondylitis, which primarily affects the lower spine and can cause stiffness and pain.
Symptoms of back arthritis can include:
- Pain and stiffness: This can be constant or come and go, often worsening with activity and improving with rest.
- Reduced flexibility: Difficulty bending, twisting, or standing straight can be experienced.
- Morning stiffness: Back pain and stiffness may be most pronounced upon waking and improve with movement throughout the day.
- Joint swelling: Depending on the type and severity of arthritis, some swelling around affected joints might be noticeable.
Seeking professional help is crucial if you suspect back arthritis. A doctor can diagnose the specific type of arthritis through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to slow arthritis progression and optimize quality of life.
Embracing Treatment Options for Back Pain and Back Arthritis
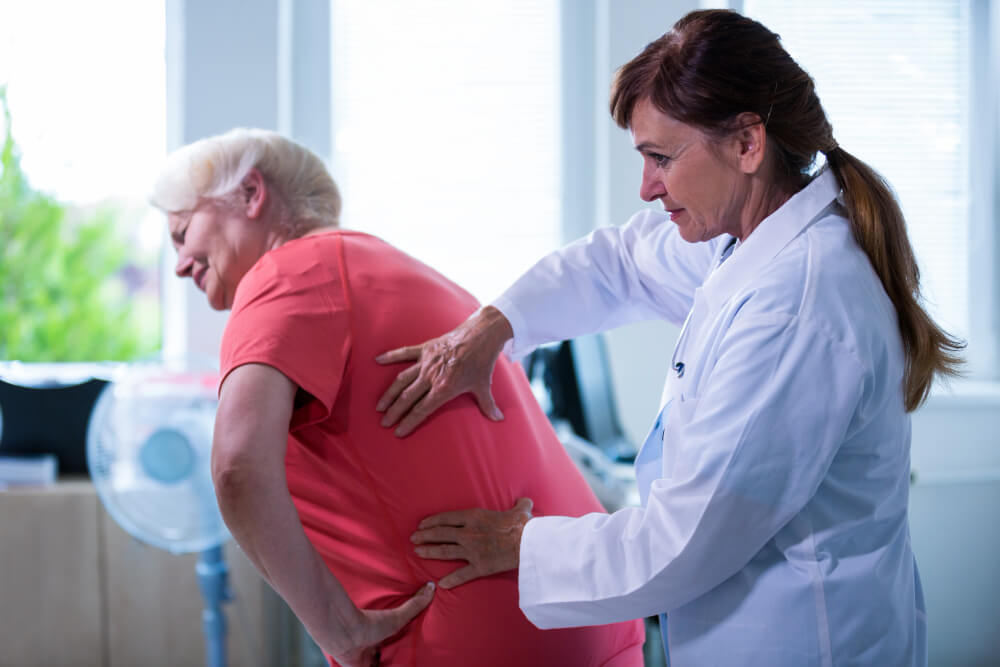
While there’s no cure for arthritis, various treatment options can effectively manage back pain and improve overall well-being. Here’s an overview of some widely used approaches:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These over-the-counter or prescription medications help reduce pain and inflammation. Common examples include ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib. It’s essential to consult a doctor before taking NSAIDs, as they can have side effects like stomach upset and heartburn, especially with long-term use.
- Corticosteroid Injections: These powerful anti-inflammatory injections can provide targeted pain relief and are often used for short-term management of severe flare-ups. However, repeated injections can weaken surrounding tissues and may not be suitable for everyone.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance joint stability. These exercises can significantly improve pain, function, and overall well-being.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and adopting ergonomic practices at work and home can significantly reduce strain on the spine and alleviate back pain.
- Complementary Therapies: Some people find relief with alternative approaches like acupuncture, massage therapy, and yoga. While evidence for their long-term benefits is varied, they may offer additional support and pain management.
- Assistive Devices: Using canes, braces, or walking sticks can help improve stability, support the back, and reduce pressure on affected joints, leading to improved pain management and function.
- Surgery: In severe cases with significant pain and limited improvement with other treatments, surgery might be considered. This is typically reserved for specific situations and should only be undertaken after careful discussion with a qualified medical professional.
- Maintaining a Positive Outlook: Living with chronic pain can be challenging, but maintaining a positive outlook and adopting stress management techniques like meditation, relaxation exercises.